Different UHF RFID Tags for RFID Asset Tracking
UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) RFID tags have become the cornerstone of modern asset tracking systems due to their long read range, fast data transmission rates, and ability to scan multiple tags simultaneously. From warehouses and hospitals to construction sites and IT data centers, UHF RFID tags enable businesses to monitor and manage assets with unprecedented precision and automation.
However, not all UHF RFID tags are created equal. The success of any RFID asset tracking system depends heavily on selecting the right type of UHF RFID tag that matches the application, environment, and asset material. This article will explore the various types of UHF RFID tags, their form factors, capabilities, and industry use cases in exhaustive detail.
1. Basics of UHF RFID Technology
1.1 UHF Frequency Range
- UHF RFID typically operates in the range of 860 MHz to 960 MHz.
- The actual range used varies by country (e.g., 865–868 MHz in Europe, 902–928 MHz in North America).
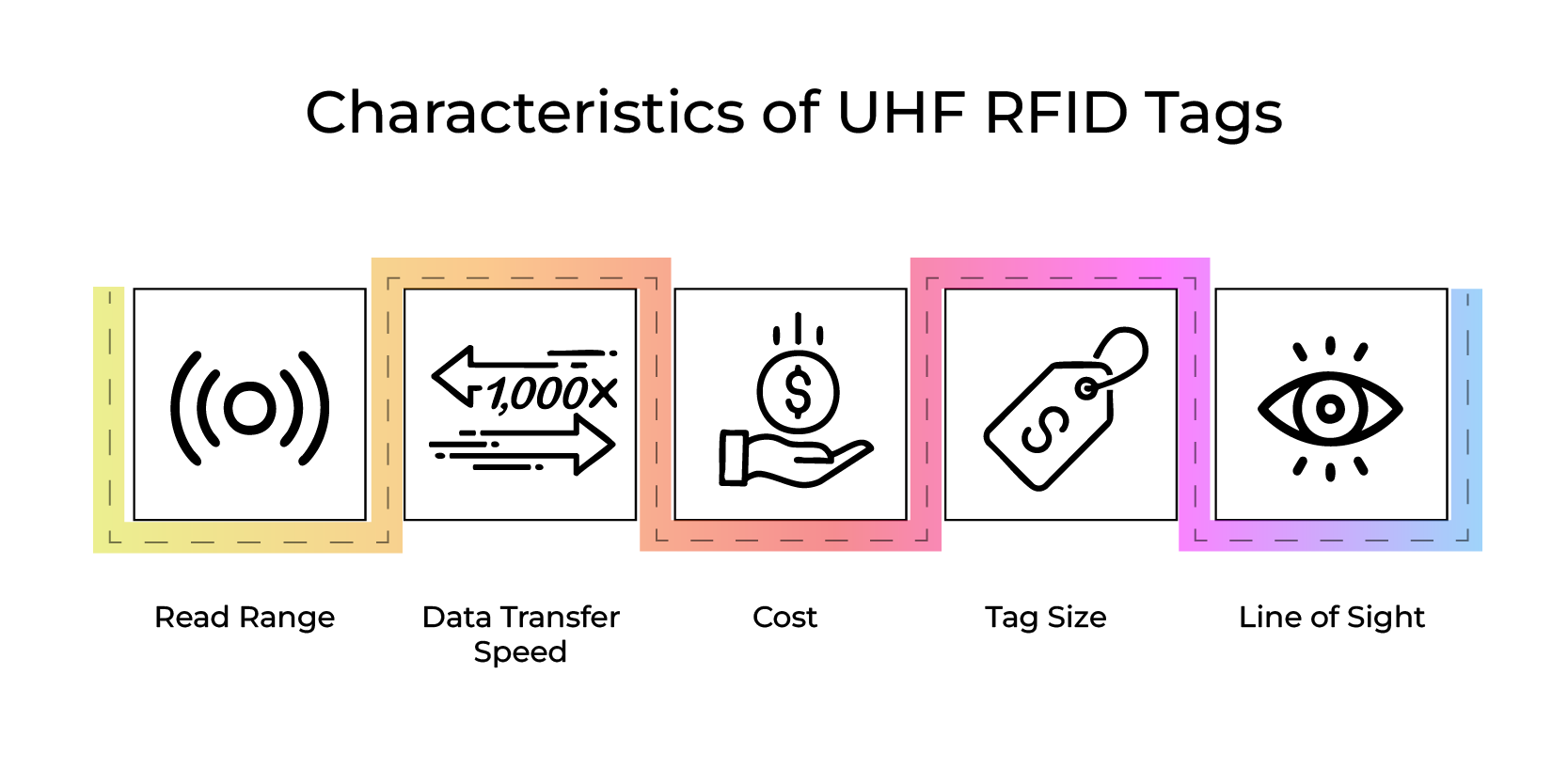
1.2 Characteristics of Passive UHF RFID Tag
- Read Range: Up to 12 meters (passive), even longer with active tags.
- Data Transfer Speed: Fast read rates, suitable for scanning hundreds of tags per second.
- Cost: Typically lower than active RFID tags.
- Tag Size: Compact, many form factors.
- Line of Sight: Not always necessary, but it improves performance.
2. Types of UHF RFID Tags for Asset Tracking
Passive UHF RFID Tags
- No onboard power source.
- Powered by the electromagnetic energy transmitted by the RFID reader.
- Most common type for asset tracking due to cost-efficiency.
- Read range: Up to 12 meters, depending on antenna size and environment.
Popular Passive Tag Subtypes:
- RFID Labels
- Consists of an antenna and chip mounted on a thin plastic substrate.
- Used for label-type tags (sticker form).
- Cost-effective and used in high volumes.
- Printable with RFID printers for barcodes, text, and human-readable info.
- Hard RFID Tags
- Rigid encasement (plastic, ceramic, metal).
- Designed for harsh environments.
- Often screw- or rivet-mounted.
- On-Metal RFID Labels
- Designed specifically to be mounted on metallic surfaces.
- Standard tags fail on metal due to RF detuning; on-metal tags use specialized spacers or shielding.
- RFID Tag Form Factors
3.1 Label and Sticker RFID Tags
- Thin, flexible, and printable.
- Ideal for cardboard boxes, IT equipment, files.
- Cannot withstand harsh environments.
3.2 Hard Plastic Tags
- Ruggedized, shock-resistant.
- Used on containers, equipment, or machinery.
- Can be screw-mounted, riveted, or zip-tied.
3.3 On-Metal RFID Tags
- Specially designed for metal surfaces (pipes, machinery, tools).
- Often have foam backing or ferrite shielding.
3.4 Cable Tie Tags
Cable Tie RFID Tags, also called RFID Zip Tie Tags or RFID Strap Tags, are durable, tamper-evident tags designed to be looped and locked around items like cables, pipes, bags, containers, tools, or equipment.
They combine the functionality of a cable tie with RFID tracking, enabling fast, non-line-of-sight identification and inventory management in industrial, utility, and logistics environments.
- Combine an RFID chip with a zip-tie.
- Attach to wires, cables, pipes, irregular items.
3.5 Bolt RFID Tags:
Bolt RFID tags (also called RFID bolt seals, RFID stud tags, or screw-in RFID tags) are a specialized type of rugged RFID tag that can be bolted, screwed, or fastened directly into objects. They are designed for permanent or semi-permanent tagging of metal, wood, or plastic assets in harsh industrial or outdoor environments.
- Shaped like industrial bolts with RFID inside.
- Used in heavy machinery or construction equipment.
3.6 Nail Tags:
Nail RFID Tags (also known as RFID nail tags, RFID spike tags, or tree tags) are a type of mountable, rugged RFID transponder designed to be nailed or hammered into wood, plastic, or soft materials. These tags are ideal for long-term tracking of assets in forestry, logistics, agriculture, construction, and utility sectors.
They are especially valued in outdoor or industrial applications where adhesives, labels, or standard tags would fail due to moisture, abrasion, or exposure to weather.
- Can be hammered into wood, pallets, or trees.
- Rugged and tamper-resistant.
3.7 Embeddable RFID Tags
- Inserted inside plastic, rubber, or silicone during manufacturing.
- Ideal for tool tracking, weapon tracking, or custom asset embedding.
Key Applications of UHF RFID Tags
|
Industry |
Application |
|
Events & Festivals |
Ticketless entry, crowd control, VIP access, cashless payments |
|
Healthcare |
Patient identification, medication tracking, mother-baby pairing |
|
Fitness & Gyms |
Member ID, locker access, attendance tracking |
|
Amusement Parks |
Ride access, line skipping, contactless purchases |
|
Hospitality |
Room access, guest tracking, all-inclusive resort packages |
3.9 Tamper-Evident Tags
Tamper-evident RFID tags are specially designed RFID tags that detect or indicate tampering, removal, or unauthorized interference. These tags are widely used for asset protection, anti-theft, and security compliance in industries where integrity and traceability are critical.
- Break or deactivate when removed.
- Useful for sealing containers, crates, or confidential documents.
RFID Cable Holder Tag is a specialized RFID tag designed to track, organize, and manage cables, hoses, and wiring in environments where identification, safety, and maintenance tracking are critical. These tags securely attach to cables and integrate RFID technology for automated data capture.
3.11 Rubber RFID Tags
RFID Rubber Tags are a type of passive RFID tag designed specifically for rugged, flexible, and curved-surface applications. These tags are embedded in rubber encapsulation, making them ideal for harsh environments or for attachment to non-metallic curved surfaces, such as tires, hoses, cables, or industrial tools.
3.12 Linen RFID Tag
Linen RFID tags (also known as laundry RFID tags) are UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID tags specifically designed to withstand harsh laundry environments, including high temperatures, pressure, water, and chemicals. These tags are embedded in or attached to linen, uniforms, towels, and garments to automate and track their movement, usage, and cleaning cycles.
4. Materials and Environmental Durability
4.1 Encasing Materials
- Plastic (ABS, Polycarbonate): Cost-effective and durable.
- Ceramic: For high temperatures and metal mounting.
- Silicone/Rubber: Flexible, used for laundry or curved surfaces.
- Epoxy: Seals tags against water, dust, and solvents.
4.2 Environmental Resistance
- Temperature: Some tags withstand -40°C to +250°C.
- Waterproofing: IP67 to IP69K ratings.
- Chemical Resistance: Useful in oil, gas, or manufacturing.
- UV Resistance: For long-term outdoor use.
5. RFID Tags for Different Asset Categories
5.1 IT Assets
- Laptops, servers, routers.
- Use printable UHF labels or on-metal tags.
- Often requires asset serial and barcode integration.
5.2 Tools and Equipment
- Power tools, calibration devices, handhelds.
- Rugged, hard-shell, or on-metal tags preferred.
5.3 Furniture and Office Assets
- Chairs, desks, storage units.
- Use hidden or aesthetic label tags.
5.4 Medical Equipment
- Sterilizable, chemical-resistant tags.
- Miniature form factors for infusion pumps, carts.
5.5 Vehicles and Machinery
- Bolt or hard tags mounted on chassis or engine block.
- Use active tags for fleet tracking.
5.6 Pipes and Cylinders
- On-metal, cable tie, or nail tags.
- Must resist pressure and outdoor conditions.
5.7 Uniforms and Laundry
- Washable RFID laundry tags (woven or sewn into fabric).
- High resistance to water, heat, and detergents.
6. Mounting Methods
- Adhesive Backing: Easy to apply; limited to smooth surfaces.
- Screw or Rivet: Permanent mounting; great for rugged environments.
- Cable Tie: Versatile, non-permanent.
- Welding or Embedding: Used in manufacturing and automotive sectors.
- Epoxy Adhesive: Strong industrial-grade bond for harsh conditions.
7. Industry Use Cases
7.1 Manufacturing
- Track tools, machinery, raw materials.
- Rugged tags for metal surfaces and high temperatures.
7.2 Logistics and Warehousing
- Track pallets, crates, containers.
- Use label, hard, or reusable tags.
7.3 Oil and Gas
- High-temp and chemically resistant tags.
- Use ceramic or epoxy-sealed hard tags.
7.4 Healthcare
- Asset visibility of infusion pumps, wheelchairs, diagnostic devices.
- Use sterilizable or tamper-evident tags.
7.5 Education and Government
- Track computers, projectors, lab gear.
- UHF labels or on-metal tags.
7.6 Construction
- Monitor tools, generators, scaffolding.
- Use bolt, cable tie, or nail tags.
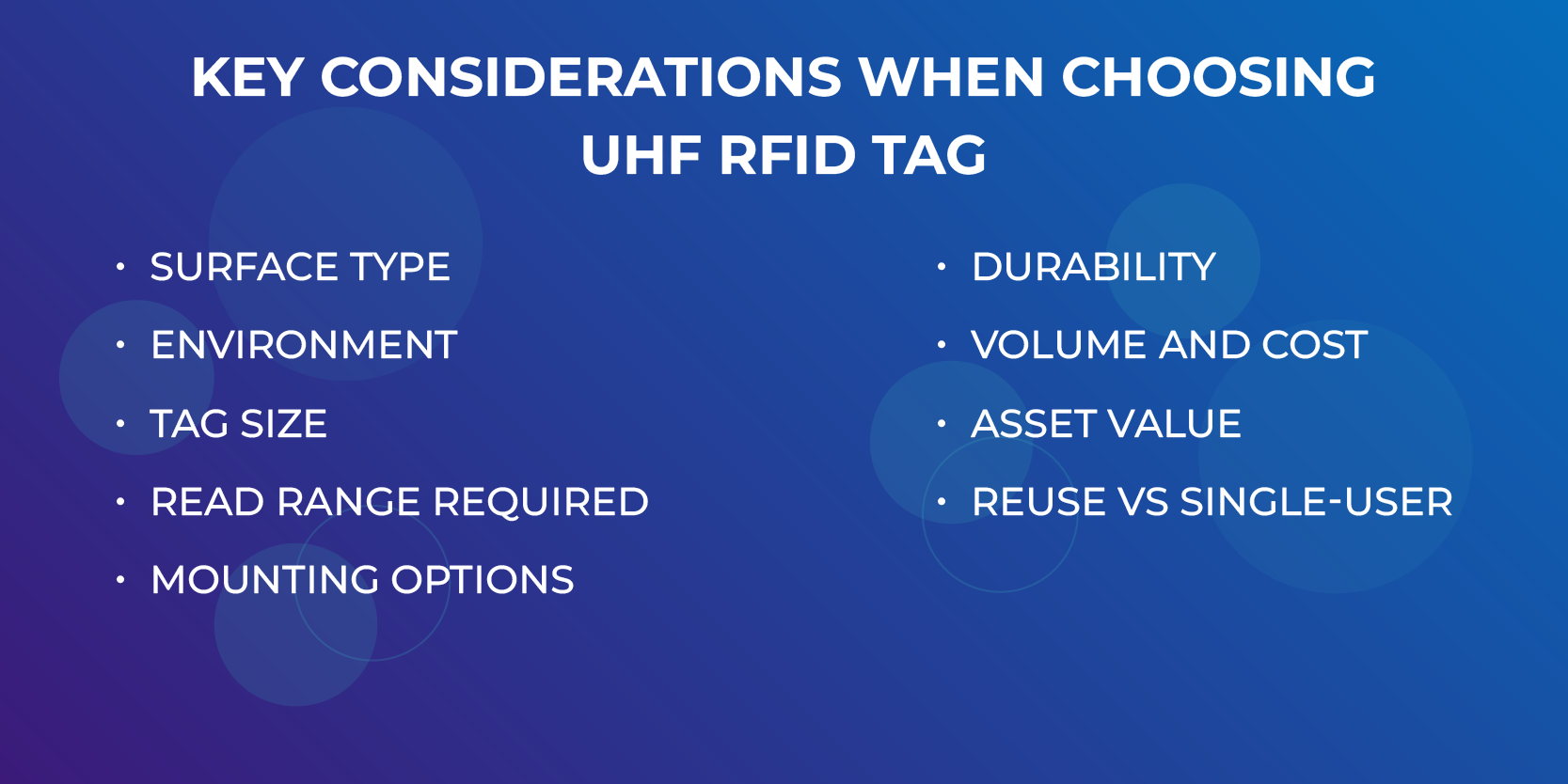
8. Key Considerations When Choosing a UHF RFID Tag
|
Factor |
Description |
|
Surface Type |
Metal, plastic, wood, glass—determines tag compatibility. |
|
Environment |
Exposure to temperature, water, dust, chemicals. |
|
Tag Size |
Space available on asset; impacts read range. |
|
Read Range Required |
Determine if 1 meter is enough or 10+ meters needed. |
|
Mounting Options |
Adhesive, screws, zip ties, embedding. |
|
Durability |
Resistance to mechanical, environmental, and chemical damage. |
|
Volume and Cost |
Higher quantities reduce per-unit tag cost. |
|
Asset Value |
Use hard or tamper-evident tags for high-value items. |
|
Reuse vs Single-use |
Labels for one-time use, hard tags for long-term. |
9. RFID Tag Standards and Compliance
- EPCglobal Class 1 Gen 2 / ISO 18000-6C
- Most commonly used standard for passive UHF tags.
- Ensures interoperability across readers and tags.
- GS1 Standards
- Provides data encoding structure (EPC, SGTIN).
10. Top UHF RFID Tag Manufacturers
- TagMatiks RFID Tags
- Tron RFID Labels
- Impinj RFID Tags
- Zebra RFID Tags
TagMatiks RFID Tags
TagMatiks RFID tags offers a broad range of UHF RFID tags optimized for use with their RFID software suite. Their tags are designed for applications such as IT asset tracking, tool tracking, manufacturing, healthcare, and supply chain.
Key Features:
- Wide variety of form factors: labels, hard tags, metal-mount, and specialty tags.
- Pre-encoded & serialized options compatible with TagMatiks software.
- Metal-mount options for challenging environments (e.g., TM-Metal, TM-AT).
- Tamper-evident & printable tags available.
2. Tron RFID Labels
TronRFID provides cost-effective UHF RFID labels primarily used in retail, logistics, apparel, and general-purpose applications. They are known for producing reliable, low-cost RFID inlays and stickers.
Key Features:
- Economical pricing
- EPC Gen 2 (ISO 18000-6C) compliance
- Wide range of inlay sizes and chip types (e.g., Monza R6, Impinj M730)
- Thermal-transfer printable labels
- Impinj RFID Chips
Impinj does not manufacture tags but provides RFID tag chips (ICs) used in thousands of inlays made by partners (e.g., Avery Dennison, Smartrac). Their chips are industry-leading in performance.
Key Chip Families:
- Monza R6, R6-P: High-speed encoding, good memory
- M730, M750: Next-gen chips with better sensitivity, performance
- Monza X: For integration with sensors or hybrid use
- M780, M781: Enhanced memory and authentication features
4. Zebra RFID Tags
Zebra offers a robust selection of RFID labels and tags, including general-purpose and on-metal options. Their tags are often used in conjunction with Zebra printers and RFID readers.
11. Emerging Trends in UHF RFID Tags
- Miniaturization – Micro tags for medical or embedded use.
- Flexible Electronics – Printed tags for wearables.
- Eco-Friendly Tags – Biodegradable or recyclable RFID tags.
- Dual-Frequency Tags – UHF + NFC for consumer and backend integration.
- Sensor Integration – RFID tags with temperature, vibration, or humidity sensors.
12. TagMatiks AT
TagMatiks AT is part of the TagMatiks platform and is geared toward efficient asset lifecycle management using technologies like UHF RFID and barcodes. It helps businesses track physical assets such as IT equipment, tools, inventory, and high-value items with real-time visibility and automation.
These RFID tags are compatible with TagMatiks AT RFID software.
Conclusion
UHF RFID tags offer a wide spectrum of options for tracking every kind of asset imaginable. Choosing the right tag is critical to ensure reliable performance, data accuracy, and return on investment. Factors like material compatibility, read range, durability, and environment must be carefully considered before deployment.
From lightweight printable labels to rugged industrial hard tags, the UHF tag ecosystem is versatile and continuously evolving. With the right strategy and tag selection, businesses can achieve end-to-end asset visibility, loss prevention, and operational efficiency like never before.
Recent Posts
-
Different UHF RFID Tags for RFID Asset Tracking
UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) RFID tags have become the cornerstone of modern asset tracking systems du …Jun 2nd 2025 -
Impinj R700 UHF RFID Reader: Comprehensive Guide
The Impinj R700 UHF RFID reader represents a significant advancement in fixed RFID reading technolog …May 26th 2025 -
RFD40 UHF RFID Sled: A Comprehensive Overview
In today’s fast-paced retail, logistics, healthcare, and warehousing environments, the need fo …May 20th 2025




