Best RFID Tags for Metal Environments: Types & Applications
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is revolutionizing asset tracking, inventory management, and supply chain processes. However, metal environments have traditionally posed challenges for RFID systems due to signal reflection, interference, and absorption. To overcome these obstacles, specialized RFID tags—commonly known as on-metal tags or metal-mount RFID tags—have been developed to perform reliably in harsh industrial and metallic settings.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore different types of RFID tags designed for metal environments, how they work, their advantages and limitations, and ideal use cases.
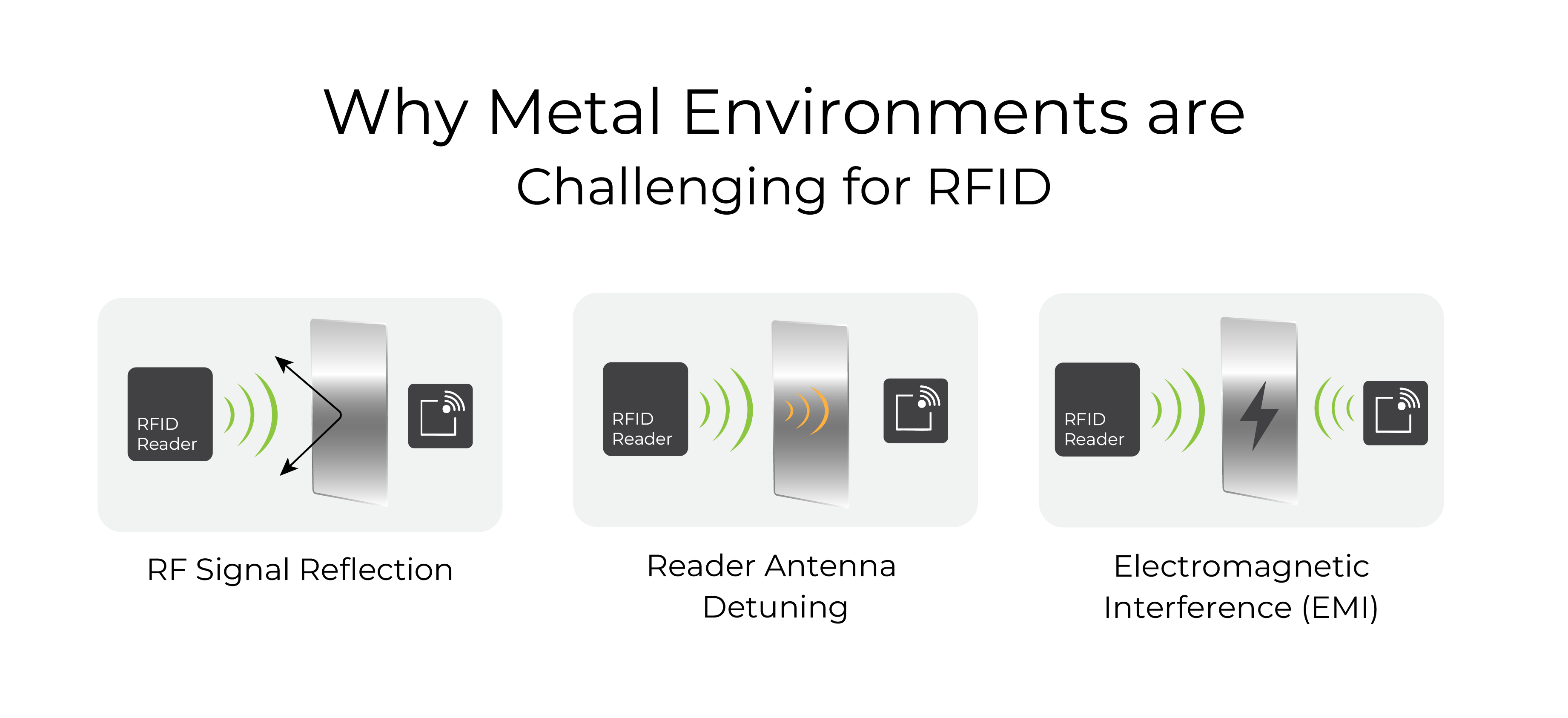
Why Metal Environments are Challenging for RFID
Before diving into tag types, it's important to understand why metal environments are problematic for conventional RFID tags:
- RF Signal Reflection: Metal reflects radio waves, leading to multipath interference.
- Signal Absorption: Metal can absorb or detune RFID signals, reducing read range.
- Reader Antenna Detuning: Proximity to metal alters antenna impedance, reducing performance.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Machines and electrical equipment create EMI that distorts signals.
How RFID Tags for Metal Work
RFID tags for metal environments are engineered with special materials, spacers, or shielding layers that allow the tag to operate on or near metal surfaces. These tags are typically constructed in ways that:
- Isolate the antenna from the metal surface.
- Use tuned antennas that exploit the reflective properties of metal.
- Include ferrite or foam backing to reduce interference.
- Optimize read performance using tuned frequency responses.
Categories of RFID Tags for Metal Environments
1. On-Metal UHF RFID Hard Tags
These are rugged, mountable tags designed specifically for direct application on metallic surfaces.
Features:
- ABS or polycarbonate Engineering Plastic casing for durability
- Foam or ferrite backing layer
- Long read ranges (up to 10 meters, depending on the reader and surface)
Examples:

Use Cases:
- Industrial asset tracking (pipes, valves, tools)
- Military and aerospace equipment
- Returnable transport items (metal crates, kegs)
- Printable On-Metal RFID Labels (Silver Labels)
These are thin, printable, adhesive-backed RFID labels designed to work on metal surfaces.
Features:
- Typically 1–3 mm thick
- Printable with RFID-enabled printers (like Zebra ZT411)
- Often based on foam or ferrite insulation
- Easy to apply, like a sticker
Examples:
- TagMatiks Pre-printed/Pre-encoded On Metal Blade II RFID Labels - 2.36" x 0.98" x 0.047"
- TagMatiks Pre-printed/Pre-encoded On Metal RFID Labels—1.8" x 0.7" x 0.06"
Use Cases:
- IT asset tracking (laptops, servers)
- Laboratory equipment
- Healthcare devices
- Office equipment tagging
- RFID Tool Tags
RFID Tool Tag Features:
- Durable & Rugged: Built to withstand harsh environments (water, dust, impact).
- Compact Size: Small and lightweight to fit on tools easily.
- Attachment Options: Screws, adhesive, zip ties, or magnetic mounts.
- Frequency: Mostly UHF for longer range; some HF for close range.
- Read Range: From a few cm to 10+ meters depending on setup.
- Memory: Stores unique ID and sometimes extra data (e.g., maintenance info).
- Metal-Friendly: Special tags for metal tools to avoid interference.
- Environmental Resistance: Often waterproof and chemical-resistant.
Example:
RFID Tool Tag Use Cases:
- Tool Tracking & Inventory: Quickly locate and manage tools.
- Maintenance Records: Track servicing and calibration schedules.
- Checkout Systems: Manage who uses tools and when.
- Workflow Optimization: Monitor tool usage in jobs or production.
- Safety Compliance: Ensure only safe, calibrated tools are used.
- Automated Tool Cribs: Auto dispense and return tools.
- Quality Control: Audit tool usage for product quality.
- Magnetic Mount RFID Tags
These tags feature magnetic backings allowing for temporary placement on metal surfaces without adhesives or screws.
Features:
- Easily removable and reusable
- No drilling or adhesives required
- Good for returnable assets
Use Cases:
- Toolroom inventory
- Temporary asset tracking
- Reusable containers and bins
- Embedded On-Metal RFID Tags
These tags are integrated directly into metal objects during manufacturing or post-production.
Features:
- Compact and tamper-proof
- Often encased in epoxy or resin
- Designed for minimal visibility and maximum durability
Examples:
- TagMatiks Pre-printed/Pre-encoded On Metal RFID Labels (Tamper Proof)
- TagMatiks Pre-printed/Pre- encoded On Metal RFID Labels
Use Cases:
- Surgical instruments
Defense and aerospace component - Industrial molds and tooling
Key Selection Criteria for On-Metal RFID Tags
When choosing RFID tags for metal environments, consider the following:
|
Criteria |
Considerations |
|
Mounting Surface |
Flat, curved, or irregular surfaces |
|
Attachment Method |
Adhesive, screw, weld, magnetic, embedded |
|
Durability |
Resistance to heat, chemicals, moisture, mechanical stress |
|
Read Range |
Required distance (from 10 cm to 10 m) |
|
Size and Form Factor |
Space available on the object |
|
Printing Requirements |
Do you need human-readable info or barcodes printed? |
|
Cost |
Volume, application importance, reuse potential |
Common Applications of RFID on Metal
|
Industry |
Application |
|
Manufacturing |
Tool tracking, machine maintenance records |
|
Oil & Gas |
Pipe and valve identification, asset lifecycle management |
|
Healthcare |
Tracking surgical kits and reusable equipment |
|
IT & Data Centers |
Server and hardware identification |
|
Aerospace |
Tracking metal parts and assemblies |
|
Construction |
Heavy machinery tracking, scaffolding monitoring |
|
Automotive |
Engine and chassis part identification |
Challenges and Considerations
- Tag Orientation: Performance can drop if tag orientation isn't optimal for the reader's antenna.
- Reader Compatibility: Ensure reader antennas support UHF frequencies tuned for metal-tag optimization. Generally on metal tags are regional, so ensure reader and tag are of same frequency band ( rephrase it)
- Environmental Factors: Choose tags based on exposure to elements like heat, dust, vibration, and liquids.
- Cost vs. Performance: Durable metal-mount tags can be more expensive—choose based on lifespan and ROI.
Conclusion
RFID tags designed for metal environments have unlocked a wide range of possibilities for industries dealing with heavy machinery, metal surfaces, and complex assets. From rugged hard tags to printable labels and embedded solutions, the right RFID tag can ensure accurate tracking, real-time visibility, and operational efficiency even in the harshest conditions.
When implementing an RFID solution in a metal-rich environment, choosing the right tag is as critical as selecting the right reader and software. With a deep understanding of your use case and the right tag type, RFID can transform your operations—regardless of how metallic the setting is.
Recent Posts
-
How RFID Handheld Readers Can Be Used with GPS for Asset Location Tracking
Asset tracking has become a critical challenge across industries such as logistics, warehousing, hea …Feb 26th 2026 -
How to Choose the Best RFID Printer: A Complete Buyer's Guide
1. What is an RFID Printer (and Why Do You Need One)? An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) print …Feb 17th 2026 -
Zebra RFD40-M Premium Plus UHF RFID Sled
The Zebra RFD40M Premium Plus UHF RFID Sled is a modular, high-performance RFID reader that attaches …Feb 9th 2026




